Are you wondering how to stop receding gums? When your gums recede, they pull back over the tops of your teeth, exposing sensitive parts of your teeth, and sometimes even parts of your roots.
Not only does this have negative aesthetic implications, but it can also lead to sensitivity and other oral health problems.
So, if you’re worried about receding gums and want to know what to do about them, you’re in the right place.
In this article, we will explain what causes receding gums, other symptoms to look out for, and possible treatments to repair your gum tissue and improve your overall gum health.
We hope this helps you make informed decisions about your dental care and treatment.
If you’d like to get advice from a dentist right away, you can chat with a dentist online for free using Denteractive’s teledentistry service.

In This Article
What should my gums look like?
Let’s begin with what exactly healthy gums look like — color isn’t a sure-fire way to determine whether gums are healthy or not. You know how we all have different levels of melanin in our skin? Well, we all have different levels of melanin in our gums, too!
That means that people with darker skin may have darker gums and people with lighter skin may have lighter gums—in fact, healthy gums can range in color from pink to brown and black.
However, any sudden or drastic changes in the color of your gums may be an indication that something is wrong.
But there are other ways to determine if your gums are healthy. In general, healthy gums:
- Are firm
- Lie just against your teeth
- Don’t bleed when you brush or floss your teeth
If your gums are swollen, form large pockets around the tops of your teeth, or have the tendency to bleed, then they need some TLC and maybe even medical intervention.
So, how do you treat receding gums or reverse receding gums, medically or at home? Keep reading to find out!
What are receding gums?
Gum recession refers to a condition in which gums draw back from the teeth, leaving the roots of your teeth exposed. This condition is also called gingival recession.
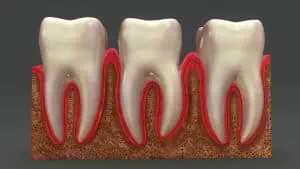
There are various symptoms of gum recession. These include:
- Increased sensitivity in your teeth
- Teeth that appear longer than normal
- A notch or pocket on your gum line (the area where the gum meets the tooth).
Gum recession is a very common dental problem, in fact nearly half of adults over 30 have it, but it should not be ignored as it is an indication of serious underlying gum disease.
Why do gums recede?
What causes receding gums in most people? There are a handful of reasons, including gum disease, forceful brushing, injury or teeth grinding. Let’s go over them now!
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is the infection and inflammation of gums and other tissues in the mouth. The bacteria start building up in your gum tissue along with other debris to form plaque which causes the gums to inflame.
Factors that may contribute to periodontal disease include:

- Lack of oral hygiene causing increased bacterial buildup
- Crooked teeth
- Faulty or damaged fillings
- Ill-fitting dentures or bridges
- Using a medication that can cause dry mouth
- Hormonal imbalance or changes due to physiological conditions such as pregnancy or oral contraceptives
- Smoking or chewing areca nuts
- Certain medical conditions such as diabetes
There are two stages of periodontal disease:
1. Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the inflammation of gums which may also lead to swelling, redness, and even bleeding gums. Gingivitis, if not treated, may lead to periodontitis, so you should treat receding gums as soon as possible. Gum disease may sometimes require gum surgery, which you can read more about here.
If you want to know more about gingivitis, you can read our full guide here.
2. Periodontitis
Periodontitis usually follows gingivitis, setting the stage for your gums to recede. When this occurs, your gums and connective tissue start pulling away from your teeth, leading to the formation of pockets between the tooth and gums.

These pockets harbor bacteria over time, exacerbating the inflammation. In advanced stages, you may even lose a few teeth due to continued bone loss and erosion.
Forceful or incorrect brushing
As much as regular brushing is important for maintaining good oral hygiene, using incorrect brushing techniques can actually damage your teeth.
The part of your gum that comes in contact with the crown of the tooth is called the gingival margin. Vigorous brushing can damage this area, triggering inflammation and gum recession along with other dental issues.
Some incorrect brushing factors that can lead to gum damage and recession include:
- Brushing your teeth with too much pressure
- Using a toothbrush with hard bristles
- Brushing your teeth in long, horizontal strokes
Teeth grinding and clenching

Some people have a habit of grinding their teeth as they sleep. This puts a lot of pressure on the gums, and may ultimately lead to gum recession over time.
Grinding and clenching your teeth can make them loose in their sockets and create deep pockets between the tooth and gum for bacteria to accumulate and flourish. These bacteria make the gums inflamed, and ultimately, gum recession occurs. Read more about what to do if you have a loose tooth.
Injury
A direct injury to the gum tissue can cause recession in the injured area. These injuries could happen:
- While playing contact sports
- In a fall or accident
- During a dental procedure
- From wearing partial or ill-fitting dentures

How to fix receding gums
Treatment of your receding gums depends on the underlying cause. Periodontists specialize in the treatment of gum disease, so if your gum recession is severe, your dentist may refer you to a periodontist. The following are some treatment options that can help reattach or restore gum tissue.
Gum graft surgery
Gum graft surgery is a surgical technique that can stop bone loss and gum recession from occurring any further. In addition, it may also protect the previously exposed root from decay.
Multiple types of gum grafts are available and the choice usually depends on your individual needs and the extent of the damage. Your dentist will discuss different types of grafts available with you to find the best option for you.
The procedure is made pain-free with the help of local anesthesia. During the surgery, some of the existing gum might also have to be lifted away to expose and clean the root of the tooth.
There are four different types of gum graft surgery:
- Connective tissue graft
- Free gingival graft
- Pedicle (lateral) grafts
- Allograft
The final option, allograft, is when healthy tissue is taken from another person. This may be a good option for patients who are concerned about taking their own healthy tissue from their palate to perform the graft, or for those who don’t have enough tissue for grafting.
Pinhole surgical technique
Pinhole surgical technique (PST) is an innovative surgical treatment for receding gums. During PST, your dentist makes a tiny hole in your gum tissue above the exposed tooth root.
This is followed by the separation of the gum from your tooth root with the help of a special tool. The gum is then stretched and repositioned over the exposed tooth root.
The best treatment for stopping gums from receding depends on each case, and some cases may require a graft, as recommended by your dentist.
Gum graft surgery won’t be enough to stop the problem for good, as it’s also essential to address the underlying cause of gum recession so that it doesn’t continue to happen. Some solutions to common causes include:
- Getting a mouthguard to stop teeth grinding at night.
- Improving poor brushing techniques.
- Correcting malocclusion that’s making it hard to properly clean gums.
Dr. Reshad, Sutton Place Dental Associates
How to fix receding gums without surgery
It may be possible to fix receding gums without surgery in some cases, using any of the following techniques:
- Desensitizing agents, varnishes, and dentin bonding agents: All these products are used to decrease the sensitivity of an already exposed tooth root. These agents not only treat the nerve symptoms but also play a role in oral hygiene by making the brushing of sensitive teeth much easier.
- Pink porcelain or composite: This is a material that matches the color of your gums and can be used to fill the gap between your gums and teeth.
- Removable gum veneers: In patients with large areas of missing gum tissue, gum veneers may be used to protect the damaged gums. These are mostly made of acrylic and silicone materials.
- Composite restoration: Tooth-colored composite resins are also used to cover the exposed surface of the root. This also closes the gap between teeth and gums.
- Orthodontics: Repositioning is another way to reduce gum recession. Different processes are used to position the gum tissue back over the tooth slowly while correcting the gum margin.
- Scaling and root planing: Some of the primary treatments that your dentist would recommend for gum recession are scaling and root planing. This is like a deep cleaning for your teeth. In these procedures, plaque and tartar that can’t be removed by normal brushing are taken off from below the gum line. The roots are then smoothed with a special instrument that helps reattach the gum and tooth.
If you think you might need treatment for gum recession but you’re worried about getting surgery, you can begin with a dentist consultation. If you need help finding a dentist near you to fix receding gums, you can call 866-383-0748. Live operators are standing by, 24/7, ready to connect you with a dentist in your area.
You can also have a look at our full guide on how to find a periodontist near you.
How much does it cost to fix receding gums?
There are various treatments for receding gums. Sometimes you may have to combine multiple treatments. Have a look at the following table to see what you might have to pay to fix your gums:
Procedure | Pricing |
Gum graft | $600–$1200 |
Traditional porcelain veneer (90.5 mm thickness) | $700–$1300 per tooth |
Veneer (0.2–0.3mm thick) | $700–$1300 per tooth |
Pinhole surgical technique | $1600–$3200 |
Can receding gums grow back?
‘Can receding gums be reversed?‘ is a common question regarding this condition. In short, no, receding gums cannot be reversed; nor can they grow back, but there are treatments that can help.
However, with the help of various gum recession treatment options, you can definitely stop further progression. There are also some natural remedies that may help soothe the underlying condition and stop further advancement of this issue that we will discuss in the next section.
Natural remedies for receding gums
There are some natural remedies that can help prevent gum recession, although you should also consult your dentist to see whether professional treatment is required.
- Eucalyptus oil: According to some research, eucalyptus oil acts as an anti-inflammatory agent and stimulates new gum tissue, thereby maintaining appropriate oral health and stopping gums from receding.
- Green tea: A study performed in 2009 showed that green tea may have benefits for teeth and gums. Try drinking two cups of green tea a day, or use it as a daily mouthwash.
- Septilin: Septilin is an herbal mix of guggul, guduchi, licorice, and some other ingredients and has been shown to have potential cleaning benefits and reduces the chances of tooth loss. This has been proven by a 2014 clinical trial published in the Journal of Periodontal Implant Science.
- Hydrogen peroxide: If you have sore, red, and swollen gums, a hydrogen peroxide mouthwash may help reduce some symptoms and can eliminate some strains of bacteria that cause gum disease. To make this solution, mix 60ml of 3% hydrogen peroxide with 60ml of water and rinse this mixture around in your mouth for about 30 seconds. Repeat this procedure about 2-3 times a week and avoid swallowing the solution. Many people consider this solution the best mouthwash for receding gums.
- Mouthwash for receding gums: There are many mouthwashes you can buy to help improve gum health, like CloySYS Healthy Gums Oral Rinse, which soothes gums and eliminates bacteria. Read our guide to the best toothpaste for gums for some more tips.
None of these natural remedies should be used in place of treatment from your dental professional. Mouthwashes or hydrogen peroxide rinses may supplement treatment but cannot replace it, and we recommend you speak with your dentist before trying any home remedies.
How to stop receding gums from getting worse
Use correct brushing techniques

To stop receding gums from getting worse, it is imperative to use correct brushing techniques. The following guidelines are provided by the American Dental Association:
- The toothbrush should be placed at an angle of 45 degrees against the gums.
- The toothbrush should be moved back and forth against the teeth in small tight strokes, with the application of gentle pressure.
- Hold the brush vertically when you are cleaning the inner surface of the front teeth.
- The chewing surface of the teeth should not be ignored while brushing.
- Teeth should be brushed for a total of two minutes.
Many people find it helpful to switch to an electric toothbrush for healthier gums. The CariPRO Ultrasonic, in particular, is good for gum health for a few reasons:
- 2-minute auto-timer with 30-second quadrant notification
- Special gum care cleaning mode
- DuPont bristles are cut and angled to optimize gum health
Find out more about the CariPRO in our full review, and you can also have a look at our complete guide on how to brush your teeth!
Wear a mouthguard
Teeth grinding can be prevented by wearing a mouthguard. Mouthguards not only help apply an even amount of pressure across the jaw, but they also act as a physical barrier to prevent teeth grinding.
It’s also important to wear a mouthguard while playing contact sports to prevent injury to the teeth and gums.
Replace ill-fitting dentures
Ill-fitting dentures may cause gums to recede due to continual rubbing. This can be prevented by replacing partial dentures whenever needed.
Visit the dentist regularly
Regular visits to a dentist can prevent gum damage with early diagnosis and treatment. Moreover, any ill-fitting dentures should also be replaced.
In the video below dental hygienist, Teeth Talk Girl, summarizes some of the key ways to prevent gum recession and gum disease in general.
Conclusion
Gum damage, once occurred, is nearly impossible to completely reverse; however, there are certain measures that can be taken to reattach and restore gum tissue around the teeth.
Good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups are the key to prevent, slow down or stop gums from receding. Talk to your dentist and get tailored medical advice about your gum treatment according to your gum condition.
If you’d prefer to speak with a dentist online before going into the office, you can also find out more about online dentistry in our separate teledentistry guide.
FAQs
Why are my gums receding?
Multiple factors can lead to gum recession. In most cases, the cause is periodontal disease, which is a bacterial infection of gum tissue and the supporting bone.
How can I prevent gum recession?

Observing good oral hygiene is the best way to prevent gum recession. Brush and floss daily and get a dental checkup biannually. There are other things you can do as well.
Quit smoking, eat a well balanced and healthy diet, and keep monitoring your gums for any changes.
How can I make my gums healthier?
If you want to take better care of your gums and you don’t yet have gum disease, you can ensure that your gums stay healthy by taking care of them and following these steps:
- Use an electric toothbrush instead of a traditional one.
- Brush your teeth in the correct way at least twice a day.
- Choose a toothbrush that has a special gum care head.
- Floss your teeth daily and massage your gums.
- Replace your current toothpaste and mouthwash with one that has fluoride.
Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology: Etiology and occurrence of gingival recession – An epidemiological study. Consulted 20th January 2020.
Journal of Periodontology: Effect of Eucalyptus Extract Chewing Gum on Periodontal Health: A Double-Masked, Randomized Trial. Consulted 20th January 2020.
Journal of Periodontology: Relationship between intake of green tea and periodontal disease. Consulted 20th January 2020.
Journal of Periodontal and Implant Science: Herbal anti-inflammatory immunomodulators as host modulators in chronic periodontitis patients: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Consulted 20th January 2020.
National Journal of Maxillofacial Surgery: Comparative evaluation of topical application of turmeric gel and 0.2% ochlorhexidine gluconate gel in prevention of gingivitis. Consulted 20th January 2020.
ADA: Brushing your teeth. Consulted 20th January 2020.
CDC.gov: Periodontal Disease. Consulted 9th November 2021.





