Tooth decay and cavities affect the majority of people at some point in their lives. They are also largely preventable with a good oral hygiene routine and regular visits to your dentist.
If you do have tooth decay, you should not ignore it, as it will only get worse, and ultimately become a serious infection, requiring antibiotics, tooth removal, and even surgery.
So if you’re worried about having or getting rotten teeth, you’re certainly not alone. Fortunately, if caught early, it can be easy to reverse tooth decay and prevent a cavity from developing.
If left untreated, tooth decay can lead to more serious dental problems like abscesses and tooth loss.
In this guide we’ll go over the following information:
- What is tooth decay?
- What causes tooth decay?
- Tooth decay stages
- How to get rid of a cavity
- How to prevent rotten teeth
We’ll also go over how tooth decay leads to cavities and rotten teeth and ways to stop the infection developing this far.
Children with rotten teeth are also a growing concern, so we’ve included some information on how to recognize the signs or rotten teeth, what to do if your child has a cavity, and how to prevent further teeth rotting.
In This Article
What is tooth decay?
Bacteria in your mouth collect in a sticky film on your teeth known as Dental plaque. These bacteria feed off sugary foods and drinks and produce acid, which eats away at your tooth’s enamel.
The enamel, is a strong substance on the outer surface of your tooth, which your body can replenish over time. But once the build-up of bacteria reaches a certain point, your body can’t keep up and your tooth enamel starts to decay. The medical term for enamel decay and decaying teeth is dental caries, although it’s commonly referred to as rotten teeth.
Plaque most often gathers around the gum line, along the edges of existing fillings, where teeth connect, and in the ridges on the biting surfaces of teeth.
Plaque can be removed from teeth by brushing and flossing, but if left for long enough it hardens into a substance called tartar. This is a breeding ground for those acid-producing bacteria, but tartar can only be removed with a proper dental cleaning. If not removed, it can lead to gum disease, or gingivitis – often accompanied by bleeding gums.
More than 91% of US adults aged 20–64 have cavities, and a quarter of all cavities haven’t been treated. According to the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, tooth decay is the most prevalent chronic disease in both children and adults in America, even though cavities are largely preventable. Compared to countries in Asia and Europe, the US is the third-worst country for tooth erosion, just after Thailand and Singapore.
What is a cavity?
So how do cavities form? Once there is a hole in the enamel of your bad tooth, the bacteria can spread to the inner layers of the dentin and pulp, and once there, the infection can spread rapidly. The resulting hole in the tooth is called a cavity.

Simply put, we can define a cavity as a hole in a tooth that forms when decay is left to spread. It only takes a tiny hole in the tooth for a large cavity to form.
If the cavity spreads to the dental pulp inside the decayed tooth it causes pulp inflammation and starts to kill off the nerves and blood vessels. In the end, the rotten tooth itself dies and becomes discolored.
The bacteria can also form a tooth abscess at the root of the rotten tooth or in the surrounding gum tissue. The infection may eventually spread into other parts of the body through the blood stream, causing serious health problems.
Which teeth are most susceptible to cavities?
Molar cavities are more common than cavities in your front teeth. You’re more likely to have a cavity in a molar, or back tooth, than you are to have a cavity on a front tooth.
That’s because those back teeth have more grooves and creases that can collect and trap food particles.
Additionally, you’re more likely to have a molar cavity than a front tooth cavity because it can be more difficult to properly clean your back teeth. That being said, you can get cavities in any of your teeth, so make sure to take care of all of them!
What causes tooth decay?
We are all susceptible to dental caries if we don’t take care of our teeth. So how do you get cavities? Let’s go over some of the most common causes of decay in teeth:
- Consuming foods and drinks that are high in sugar or carbohydrates
- Eating a lot of citrus fruits, which are very acidic
- Drinking acidic beverages such as soft drinks and sports drinks
- Snacking in between meals
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking and vaping
- Failing to have regular dental checkups
- Not cleaning teeth properly while wearing braces
- Decay under crowns that need to be replaced
- Eating disorders like bulimia
- Breathing through your mouth too much
The good news is that these tooth decay causes are all things that you can work to improve. By controlling what you eat and drink, cleaning your teeth well, and visiting the dentist regularly for professional teeth cleaning, you can reduce the chances of your teeth decaying and developing cavities.
Remember, our teeth decay because of the bacteria contained in plaque as well as acid from other sources. If your teeth feel sticky or furry, it’s probably because of plaque, which will increase the chances of having unhealthy teeth. Try scraping your fingernail along a tooth and you might remove a white or clear substance.
The longer that plaque stays on your teeth, the more risk there is of dental decay.
Tooth decay at the gumline
Gumline cavities form when plaque builds up around the gumline and eats away at the enamel there. Sometimes this can happen when the gum tissue recedes because of periodontitis, leaving the tooth roots exposed.
Gumline cavities are treated the same way that normal cavities are treated, usually with a filling. The difference is that if a gumline cavity goes beneath the gums, then it is more difficult to access and you may need minor gum surgery.
Tooth decay under crowns
Decay under crowns happens when plaque gets trapped under crowns, or when the natural part of the tooth decays, and this decay spreads under the crown.
If this happens, you will need a new crown. You may also need a root canal if the damage has extended far enough.
Signs of tooth decay
What does tooth decay look like? In the early stages, decay will appear as a small white or brown spot on your tooth. You may not be able to notice this but your dentist knows what to look for.
That’s why it’s so important to go for regular checkups; a dentist can catch early tooth decay or an early cavity and treat it quite easily, but if you wait until you notice a hole in your tooth, the damage has already spread much further.

Aside from visible damage to your teeth, symptoms of tooth decay include:
- Toothache (although pain is usually mild at first)
- Pain when chewing or biting
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks
- Bad breath that doesn’t go away
- A nasty taste in your mouth
- Resorption of teeth as a result of decay damage
If you notice any of these tooth decay or cavity symptoms, book an appointment with your dentist so the problem can be addressed sooner rather than later.
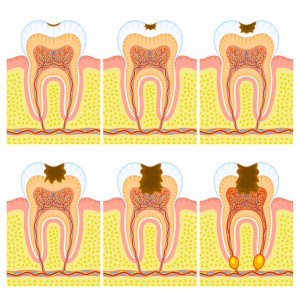
Tooth decay stages
Depending on who you ask there are 4 to 5 stages of tooth decay, but the process is the same:
- Demineralization: Demineralization is when the top layer of your teeth, called enamel, begins to weaken. When this happens, white spots will appear on your teeth
- Enamel decay: As the tooth enamel breaks down , those white spots will begin to turn brown. This is when the actual cavity will begin to form
- Dentin decay: Dentin is under your tooth’s enamel, and is much softer. Once decay reaches the decay process speeds up
- Pulp damage: Underneath the dentin is the pulp, home to blood vesels and nerves. If decay is allowed to continue, your pulp will die
- Abscess: Bacteria in the decaying pulp can cause an infection in the form of an abscess. This can spread to the rest of your mouth, through your jaw and to your head
How to know if you have teeth cavities
If there’s no pain involved yet, cavity symptoms may be subtle. In the case of a dental cavity, you may be able to see a dark spot on your tooth or feel a small hole in your tooth with your tongue or fingernail.
Cavity pain is usually more severe than early tooth decay pain because the infection has reached the nerves in the tooth pulp. However, if you ignore this pain it may disappear by itself. This doesn’t mean that the infection is gone; in fact it has spread so far that it has destroyed the nerves completely.
Other dental cavity symptoms include increased sensitivity to hot and cold foods and drinks. If you find yourself in pain when you take a sip of cold water, for example, your teeth may need some attention.
Ultimately, only your dentist can check the condition of your teeth and accurately assess how far any damage has spread. He or she will then advise you on the best course of tooth decay treatment.
Rotten teeth effects on the body
If you have tooth decay or a cavity that has been left untreated, it can actually negatively affect your overall health. According to the Mayo Clinic, some rotten teeth side effects on your health include:
- Severe pain that can negatively impact your quality of life
- Weight loss and nutrition problems due to difficulty chewing
- Tooth loss which can negatively affect your self-esteem
- Rotten teeth may lead to tooth abscesses, and this could lead to serious and even life-threatening infections
How to prevent tooth decay

The best way to avoid cavities in teeth is to prevent decay altogether. As we have already mentioned, you can stop dental decay by controlling what you eat and drink and maintaining good oral hygiene.
Here are some more tips for how to avoid cavities in teeth:
- If you do drink sugary or acidic drinks, use a straw to minimize contact with your teeth (especially during the holidays!)
- Chew sugar-free gum containing xylitol after meals if you are unable to brush (although artificial sweeteners have their risks too)
- Change your electric toothbrush head regularly – ideally every three months
- Use a fluoride or hydroxyapatite toothpaste
- Take a multivitamin that contains calcium, magnesium and vitamin D
- Take oral probiotics for adults and kids
You may also use a mouthwash that contains antibacterial ingredients and added fluoride to prevent cavities in teeth. However, many oral professionals advise not using mouthwash directly after brushing teeth. This is because it will wash away the minerals in your toothpaste, making them less effective.
Similarly, rinsing your mouth with water after you brush will dilute the ingredients in your toothpaste which are designed to protect teeth against decay.
Read more about how to brush your teeth correctly in our detailed brushing guide, or watch this short video:
In addition to proper brushing technique, you might find that you brush better with depending on the toothbrush you use. Most of us have brushing habits that we could improve, and an electric toothbrush like this one from CariPRO can help.
It has a built-in timer that lets you know how long to spend on each quadrant of your mouth, while 40,000 sonic vibrations per minute work to remove plaque. You can read our full guide to learn more about CariPRO, or try it out for yourself by clicking the button below.
How to reverse tooth decay
If you have already spotted the early symptoms of cavities, you might be wondering how to reverse tooth decay or how to fix rotting teeth without visiting the dentist.
First: Can you reverse tooth decay?
Well, the good news is, if you’re wondering how to remineralize teeth, the enamel in our teeth can remineralize itself to a certain degree and thus cure tooth decay (if you catch it early). And home remedies for tooth decay can be quite accessible, mostly having to do with your diet and oral hygiene routine.
If you cut damaging foods and drinks out of your diet and make changes to improve your oral health, this will give your enamel a chance to replenish the lost minerals and reverse tooth decay damage.

Your dentist can also provide treatments to stop decay without having to drill your tooth. These tooth decay treatments include fluoride gel, antiseptic varnish and fissure sealants. You also may want to try a full demineralization kit like this Enamel Health Kit from Dr. Brite. This will help you establish a daily oral hygiene routine that is designed to keep your enamel healthy. This kit features:
- Enamel health mouthwash
- Enmale health toothpaste
- Oral healing spray
- Breath fresheners
- Enamel health pen
All products are vegan and cruelty-free, gluten-free, SLS-free and packed full of organic and natural ingredients. And you can use code DRBRITE10 to get 10% off this and any other Dr. Brite product.
So it is possible to reverse tooth decay once it has started, as long as you catch it early. But once you have severe rotten teeth symptoms, this will no longer be the case, as you’ll learn more about below.
So, can you reverse a cavity? If you have severe tooth decay and can see a hole that reaches inside the tooth, or you are already experiencing toothache, you probably have a cavity, and will need tooth decay treatment; you can no longer cure tooth decay once it has reached this point.
And if you’re wondering how to remove tooth decay yourself—the answer is you can’t actually remove it. Your tooth will either have to remineralize naturally, or, if the decay is at the point where it needs to be removed, then that is a job for your dentist, and only your dentist.
How to get rid of cavities
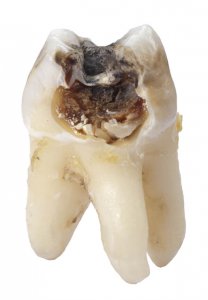
Like most of us with this problem, you’re probably wondering how to get rid of a cavity in your tooth if you have one and how to heal cavities without a filling if it’s possible. If a tooth has decayed beyond the point of natural healing, it will require a filling to stop the infection spreading any further.
The treatment process will depend on how far inside the tooth the decay has spread. Your dentist may need to take an x-ray to assess the size and extent of the cavity, especially if you have cavities between teeth that are hard to see.
If you catch the problem in the early stages, before the enamel layer has been fully eroded, your dentist may be able to remove the decay and apply a small filling without you needing an anesthetic injection. This is because there are no nerves in tooth enamel.
In cases where the infection in a rotten tooth has spread further, your dentist will administer an anesthetic to prevent pain during your tooth cavity filling. For a small cavity, treatment is usually straightforward and takes less than 30 minutes.
If dental decay has spread into the pulp chamber and tooth root, you will need root canal treatment to remove all of the decayed material. Your dentist may recommend you get a crown on your tooth to strengthen it and protect against further damage and tooth rot.
Where decay is widespread and there is very little healthy tooth left, your dentist will remove the decayed tooth completely, sometimes by oral surgery. You can avoid this by visiting your dentist as soon as you experience any tooth decay symptoms, though.
If you need to have rotten teeth extraction, your dentist will explain the options for replacing it with an artificial tooth. These include dentures, tooth bridges and tooth implants.
Using Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) to stop decay
Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) is a newly developed technology and treatment in dentistry used to prevent teeth cavities or caries from forming, growing, or spreading to other teeth. SDF is a safe, painless alternative to traditional cavity drilling procedures.
What are the ingredients in SDF?
You may be wondering what exactly is in Silver Diamine Fluoride, so we have listed the ingredients below:
- Silver: Kills bacteria
- Water: Provides a liquid base for the solution
- Fluoride: Helps your teeth rebuild (enamel repair through remineralization)
- Ammonia: Keeps the solution concentrated so that it’s as effective as possible against cavity resonance
Advantages and Disadvantages of SFD treatment
Research suggests that there is no reason for dentists to do any other type of restoration work on a patient’s teeth before treating them with SDF. It also suggests that an application of 38% SDF is needed to show a good result in enhancing dental caries management in children and adolescents. This includes the treatment of those with special health care needs.
SDF is considered effective, safe and harmless and is widely used nowadays by dentists for adolescents and children. While it has many advantages it also has some side effects. The following table will compare the advantages and disadvantages of SDF treatments:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Effective in stopping cavity development after it has formed | Can't be used for patients with a silver allergy |
Kills the bacteria that breaks down tooth enamel | Can't be used for patients with oral ulcerations or canker sores |
Alternative to drilling cavities | Can't be used for patients with extensive caries or gum diseases |
Use for dentin desensitization, caries arrest, and caries prevention | Can leave black stains around the treatment area |
Advanced research shows that SDF can be used with potassium iodide or nano-silver fluoride (NSF) which limits SDF’s black staining.
Treatment costs for a tooth cavity
There are different costs to consider when getting an estimate for filling a tooth cavity or multiple tooth cavities. Medicaid assistance programs for low-income individuals are run by each individual state, so coverage is going to vary depending on which state you live in. Medicare doesn’t cover most dental care, and this includes fillings for cavities. The good news is that if you have dental insurance, your policy might cover all or part of the costs associated with cavities:
Treatment | Purpose | Estimated cost |
Checkup | Identify problems and give oral health advice | $120 |
Apply fluoride varnish | Protect against decay | $40 |
Tooth filling | Remove decay and repair tooth | $165 |
Root canal | Remove decay deep inside tooth | $900 |
Extraction | Remove badly decayed tooth | $150 |
Crown | Protect tooth after damage or treatment | $1100 |
Bridge | Replace a missing tooth | $600 |
SDF | Stop decay from spreading | $75 |
Prices will vary depending on the size of the filling, if you have a silver cavity filling or a filling with white composite material, and where you receive treatment.
Fair Health Consumer provides detailed dental care cost estimates based on your location and whether or not you have insurance coverage.
Tooth decay in children
Sadly, 2.3 billion people around the world suffer from cavities in their permanent teeth. In poorer countries, decayed teeth are common due to the lack of available health care. According to the CDC, and highlighted here by the American Academy of Pediatrics, more than 40% of children in the US have cavities by the time they reach kindergarten.
Ways that parents can help prevent tooth decay in toddlers and children include:
- Be aware of how much sugar is in their food – not just sweet foods but things like pasta sauces and fruit juices
- Limit snacking between meals to foods that aren’t high in sugar or carbohydrates (raw vegetables and fruits are ideal)
- Supervise tooth brushing until your child is seven or older
- Consider getting a kids electric toothbrush with a timer and other fun features
- Use a toothpaste that contains fluoride
- Take them for regular dental checkups so any problems can be treated early
The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research has some more useful tips for parents on how to prevent cavities in children. This will not only lower their chances of dental decay and cavity pain; their oral health will benefit in many ways.
Children often hear things like, ‘don’t eat too much candy or you’ll get a cavity,” but it is not only children at risk for cavities and tooth decay. However, it’s not necessarily the candy that causes cavities, rather, it’s the environment sugar creates in your mouth that is the problem.
This can affect children and adults alike. Recently, it has even been shown that adults over 65 are experiencing tooth decay at a higher rate than school children. If you’re concerned about tooth decay be sure you’re:
- Brushing your teeth twice a day, two minutes each time
- Flossing each evening
- Incorporating fluoride in your routine
- Seeing your dentist every six months
Dr. Catalina Botero, Li’l Sunshine Smiles Dentistry
Treating rotten baby teeth in kids
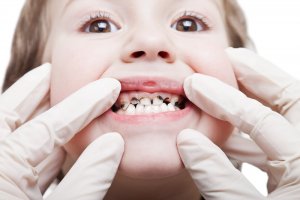
It can be distressing to realize your child has a tooth cavity, but the occurrence of kids with rotten teeth is a common problem. And the sooner you visit the dentist the greater your chances of being able to reverse the damage in the rotting tooth.
The good news is that healing teeth naturally is more possible with younger teeth. Baby teeth are particularly good at remineralizing themselves, so your toddler’s tooth decay may not require a filling.
Your dentist will advise you on how to stop tooth decay once it has started in your child’s teeth from becoming a tooth cavity. They may apply a fissure sealant, which covers the grooves in the back teeth which are particularly at risk of decay.
Dentists also recommend applying a fluoride varnish at least twice a year for children aged three and over. In order to prevent rotten teeth in toddlers, younger children may receive this treatment if the dentist thinks it is necessary.
This varnish protects teeth from bacteria and gives time for recovery from existing decay.

If your child does need a filling for a rotten tooth, it’s quite possible they won’t need an injection. If they do, the dentist will apply a numbing gel to the gum so they don’t feel any pain from the needle.
Even if you feel nervous about your child or toddler getting a filling, try to stay calm and positive. Your little one will pick up on how you are feeling. It’s very important for your kid’s rotten teeth to be treated, and if they think that visiting the dentist is a bad thing, this might deter them from seeking the dental care they need later in life.
How to heal cavities naturally
Can teeth heal naturally, and how do you get rid of cavities at home? Unfortunately, tooth decay treatment at home is only an option if the decay is caught very early, and hasn’t yet turned into a cavity. Once you have a cavity, your dentist will need to give you treatment to remove that cavity, whether with a filling or a root canal, or they may have to pull the rotten tooth completely.
If you don’t yet have a cavity, depending on which of the tooth decay stages you are in, your enamel may be able to heal naturally if you stop eating sugary foods and practice better oral health.
We can’t stress enough—if you do have a cavity, you need to go to your dentist; after you’ve progressed too far through the stages of tooth decay, no natural home remedies for cavities will be able to help.
If you want to learn more about natural ways to take care of your teeth, and how to stop cavities from happening in the first place, you can read our natural tooth care guide here.
Conclusion
Cavities are a problem that few of us will successfully avoid completely, but cavity prevention is an important aspect of dental health. Dental caries can be treated simply and even reversed if you seek treatment early on. The longer you put off visiting a dentist after you notice caries and cavity symptoms, the more extensive (and costly) your treatment for your rotten tooth is likely to be.
Follow the tips in this article for improving your oral health and managing your food and drink intake, and you should at least reduce your chances of getting a dental cavity, even if you don’t prevent tooth decay completely.
FAQs
What’s the difference between rotting teeth and cavities?
Rotting teeth is another term for decaying teeth—tooth decay is the process that happens when plaque is left too long on your teeth, the bacteria in the plaque produce enamel-eating acid.
Once that decay has worked its way through your enamel, a hole forms, and that’s your cavity.
Can cavities heal?
If your tooth decay has spread, you’re probably wondering how to heal cavities. Once you have a cavity, or an actual hole in your enamel, your cavity won’t be able to heal on its own. You’ll need to visit a dentist and they will most likely have to give you a filling to stop further tooth decay.
If you have a small cavity, treatment is straightforward and can be over in less than 30 minutes. If the infection in your rotten tooth has spread to the pulp or tooth root, it is likely you will need a root canal and maybe even extraction.
Can tooth decay be reversed?
If tooth decay is caught early, there are some ways that your body might be able to actually reverse tooth decay. Your tooth’s enamel may be able to remineralize to a certain degree.
You will need to icut out the things that are causing your tooth decay—such as a diet too high in sugar.
Your dentist may also be able to give you a fluoride gel, varnish or dental sealant to help reverse the symptoms of a decaying tooth. You may also want to consider purchasing a remineralizing toothpaste to assist in reversing the decay.
Does black on teeth mean a cavity?
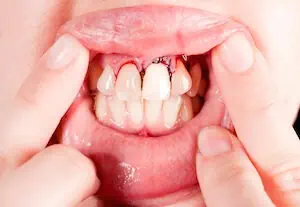
If you have small black spots on your teeth or black between teeth and it’s not caused from eating blackberries or brushing with activated charcoal, it may very well be a cavity.
Red or brown spots may mean tooth decay, and brown or black spots might be cavities.
Additionally, holes in your teeth can also appear as black tooth decay. Black rotten teeth is something that requires immediate dental care, so it’s very important that you visit your dentist if you see any of these signs.
Another cause of black-hued teeth may actually be black plaque on teeth, or black tartar on teeth. This can happen when the plaque buildup on your teeth absorbs materials from surrounding fluids in your mouth and gums that cause it to blacken.
It’s not good to have tartar on your teeth, so even if you think it’s tartar and not a cavity, you still need to go to the dentist and have it removed.
Finally, if you have black at the base of a tooth, along the gumline, this could be caused by tooth decay at the gumline, or it could be something else like gum disease.
Mayo Clinic: Cavities/tooth decay. Consulted 17th December 2024.
CDC.gov: Dental Caries and Tooth Loss in Adults in the United States. Consulted 17th December 2024.
NIDCR: Dental Caries (Tooth Decay). Consulted 17th December 2024.
American Academy of Pediatrics: Oral Health Risk Assessment Timing and Establishment of the Dental Home. Consulted 17th December 2024.
NIDCR: The Tooth Decay Process: How to Reverse it and Avoid a Cavity. Consulted 17th December 2024.
Pediatric Dentistry: Use of Silver Diamine Fluoride for Dental Caries Management in Children and Adolescents. Consulted 31st August 2024.
Sunstar: Global Healthy Thinking Report. Consulted 11th September 2024.
Who.int: Oral health. Consulted 9th November 2024.





